ErrorBoundary로 우아하게 에러 처리하기
에러 바운더리란?
에러 바운더리(Error Boundary)는 React에서 에러 처리를 담당하는 컴포넌트이다. 컴포넌트 트리의 일부를 격리하여 예기치 않은 에러로부터 애플리케이션을 보호하고 대체 UI를 렌더링할 수 있게 한다. 이를 통해 사용자 경험을 개선하고 애플리케이션 전체의 중단을 방지할 수 있다. 에러 바운더리는 React 16부터 도입되었으며, componentDidCatch 메서드를 사용하여 에러 처리를 구현한다. 이를 활용하면 안정성과 유지 보수성을 향상시킬 수 있다.
단 에러 바운더리는 다음과 같은 에러는 캐치하지 못한다.
- 이벤트 핸들러
- 비동기적 코드
- 서버 사이드 렌더링
- 자식이 아닌 에러 바운더리 자체에서 발생하는 에러
에러 바운더리를 사용하고자 한 이유
에러 바운더리를 사용함으로써 얻을 수 있는 이점에는 여러가지가 있지만 적극적으로 에러 바운더리를 사용하고자 한 가장 큰 이유는 에러 관리 포인트를 최소화 하고 싶었기 때문이다. 특히 본래의 ErrorBoundary는 데이터 페칭과 같은 비동기적 코드 에러를 캐치하지 못하지만 React Query의 defaultOptions에 useErrorBoundary:true 를 사용함으로써 서버 통신과 관련한 비동기적 에러도 ErrorBoundary에서 함께 핸들링 할 수 있다는 점에서 (리액트 쿼리의 도입과 함께) 이 점을 적극 활용하여 중앙 집중식 에러 관리를 할 수 있겠다고 생각했다.
기존에는 아래의 코드와 같은 형태로 에러를 핸들링했다.
async function getUser() {
try {
// start loading
const response = await apiClient.get<User>(`URL`);
return response;
} catch (error) {
// handle error
}
}모든 API 호출 함수마다 try-catch문으로 감싸 주었다. 이런 방식은 고전적인 방식(?)이기는 하지만 실수로 try-catch문을 빼먹을 수 있다는 휴먼에러 발생 가능성이 있다. 따라서 매번 try-catch 문으로 감싸주어야 하는 불편함과 휴먼에러의 위험성을 제거하고 중앙 집중식 에러 핸들링 하고자 하는 것이 목표였다.
만약 React Query와 같은 라이브러리를 쓰지 못하는 상황에서 ErrorBoundary로 비동기 통신 에러를 핸들링하고 싶다면 다음과 같은 방법도 있다.
function MyComponent() {
const [error, setError] = useState(null);
if (error) {
throw error;
}
useEffect(() => {
load().catch((err) => setError(err));
}, []);
return <div>...</div>;
}비동기 에러 발생시에 컴포넌트 내부에서 Error를 throw 해 ErrorBoundary에서 캐치할 수 있도록 하는 것이다. 아마 React Query의 useErrorBoundary:true 옵션을 사용하면 React Query 내부적으로 에러가 발생했을 때 에러를 throw 하도록 구현되어 있을 것이라 추측된다.
에러바운더리를 사용함으로써 장점
React의 Error Boundary를 사용하면 발생한 에러를 적절히 격리시켜 애플리케이션의 전반적인 작동에 영향을 주지 않게끔 관리할 수 있다. 이를 통해 사용자에게는 문제가 발생한 부분 대신 대체 UI를 제공하고 대처 방법을 가이드함으로써 좋은 사용자 경험을 유지할 수 있다. 또한, 에러 바운더리에서 수집한 에러 정보를 활용해 에러 원인을 신속하게 파악하고 수정하는데 도움이 된다. 이러한 장점들은 전체적인 코드의 안정성과 신뢰성을 높일 수 있다.
뿐만 아니라 대수적 효과를 지원하는 코드를 작성할 수 있게 된다. 여기서 잠깐 대수적 효과에 대해 알아보자면
💡 어떤 코드 조각을 감싸는 맥락으로 책임을 분리하는 방식을 대수적 효과라고 한다. 객체 지향의 의존성 주입, 의존성 역전과 유사하다고 볼 수 있다.
async function getUser() {
try {
// start loading
const response = await apiClient.get<User>(`URL`)
return response
} catch (error) {
// handle error }
}기존 코드의 경우, 매번 try-catch 문으로 감싸 주어야 한다는 불편함과 함께 성공하는 케이스와 실패하는 케이스의 코드가 함께 적혀있어 함수가 실제로 수행하고자 하는 동작이 가려지게 된다.
async function getUser() {
const response = await apiClient.get<User>(`URL`);
return response;
}ErrorBoundary를 사용하면 실패하는 경우의 동작은 에러 바운더리에 위임하고 데이터를 호출하는 함수는 위와 같이 순수하게 데이터만 가져오는 동작만 선언하여 사용할 수 있게 된다. Suspense를 사용하여 로딩 상태를 위임하는 것도 같은 대수적 효과로 볼 수 있다.
나타날 수 있는 에러의 종류 분류하기
그렇다면 ErrorBoundary에서 처리해야 하는 에러의 종류는 어떤 것들이 있을까? 우선 크게 예측이 가능한 에러와 예측이 불가능한 에러로 나누어 생각해 본 뒤, 각 에러에 대해 유저에게 어떤 가이드를 제공할 수 있을지에 따라 크게 4 가지로 분류했다.
- GET이 실패한 상황: data fetching에 실패하여 데이터 자체를 보여줄 수 없는 경우
- 데이터 변경 HTTP 메서드가 실패한 상황: 사용자의 액션에 정상적으로 반응하지 못 하는 경우
- 요청 권한이 없는 상황: 로그인이 끊겨 401 unauthorized 를 마주하는 경우
- unknown Error: 일시적인 네트워크 에러, 브라우저에서 발생하는 에러 등
ErrorBoundary 내부에서 각 에러 타입에 적합한 대체 UI와 유저가 에러를 해결하기 위한 가이드를 제공하도록 로직을 작성할 것이다.
에러 처리 전략
- GET이 실패한 상황: 데이터 패칭에 실패하게 되면 현재 보여 줄 수 있는 데이터가 없거나 정확하지 않은 데이터를 노출하게 된다. 부정확한 데이터를 노출하는 것은 적절하지 않다고 생각하여 대체 UI를 보여주기로 했다. 또한 대체 UI에서 다시 시도하기 버튼을 노출해 유저가 에러 상황에서 데이터 패칭을 재시도 할 수 있도록 가이드한다. 추가적으로 토스트 메세지도 노출해 주도록 하자.
- 데이터 변경 HTTP 메서드가 실패한 상황: POST, PUT, DELETE와 같은 변경 메서드는 사용자 액션에 의해 발생한다. 액션의 성공/실패 여부를 즉각 피드백 해줄 필요가 있다. 하지만, 액션이 실패했다고 하여 대체 UI를 보여줄 필요가 있을까? 사용자가 실패했다는 것을 인지하게 하고, 다시 요청하게끔 유도만 하면 될 것이다. 즉, 이 경우에는 토스트 UI만 발동시킨다.
- unauthorized(401) Error: 권한이 없어 발생하는 에러기 때문에 401 에러가 발생할 경우 로그인 페이지로 유도하려 했으나, 401 에러가 발생할 수 있는 케이스가 생각보다 다양하다는 것을 확인하고 무조건적으로 로그인 페이지로 유도하는 것은 적절하지 않다고 생각했다. (예를 들어 나의 서비스의 경우에는 비밀번호 변경 페이지에서 기존 비밀번호와 새로운 비밀번호를 적어 POST 했을 때 기존의 비밀번호가 일치하지 않으면 401을 리턴한다. 이 경우 갑자기 로그인 페이지로 유도한다면 유저는 상당히 당황스러운 경험을 하게 될 것이다 😅) 대신 토스트 메세지를 노출하여 유저가 문제를 인지하고 로그인 하거나 또는 하려던 액션을 재시도 할 수 있도록 가이드 했다.
- unknown Error: 해당 에러는 다양한 상황에 원인을 알 수 없는 에러임으로 토스트 메세지를 노출하고 대체 UI에서 메인 화면으로 이동할 수 있도록 가이드 한다.
GlobalErrorBoundary 생성하기
위에서 정의한 모든 타입의 에러를 처리할 수 있는 GlobalErrorBoundary를 생성할 것이다. GlobalErrorBoundary는 이름에 걸맞게 app.tsx에서 pageComponent 전체를 감싸 Error의 최종 방어전선의 역할을 하도록 한다.
우선 에러의 타입을 정의해 준다.
type GlobalErrorBoundaryState =
| { error: null; errorCase: null }
| { error: Error; errorCase: "unknown" }
| {
error: AxiosError;
errorCase: "unauthorized" | "axiosGetError" | "axiosMutationError";
};그리고 getDerivedStateFromError에서 각 에러 타입을 state에 업데이트 한다.
public static getDerivedStateFromError(
error: Error
): GlobalErrorBoundaryState {
// 다음 렌더링에서 폴백 UI가 보이도록 상태를 업데이트 한다.
if (!error) {
return { error: null, errorCase: null }
}
if (!(error instanceof AxiosError)) {
return { error, errorCase: 'unknown' }
}
if (error.response?.status === 401) {
return { error, errorCase: 'unauthorized' }
}
if (error.response?.config.method === 'get') {
return { error, errorCase: 'axiosGetError' }
}
return { error, errorCase: 'axiosMutationError' }
}componentDidCatch에서는 각 에러 타입에 따라 대체 UI 이외에 부가적으로 취할 액션을 정의해 준다. 나의 경우에는 AxiosError의 경우에는 서버에서 보내준 에러 문구를, unknown 에러의 경우에는 ‘알 수 없는 에러가 발생했습니다.’라는 문구를 토스트 메세지로 노출하도록 했다.
public componentDidCatch(error: Error, errorInfo: ErrorInfo) {
// 에러 리포팅 서비스에 에러를 기록할 수 있음
// logErrorToMyService(error, errorInfo)
const { error: errorState, errorCase } = this.state
if (errorState instanceof AxiosError) {
return errorMesssageHandler(errorState)
}
if (errorCase === 'unknown') {
return Toast.show('알 수 없는 에러가 발생했습니다.', { type: 'error' })
}
}대체 UI의 경우에는 axiosGetError와 unknown 에러의 경우에만 노출하고, 나머지 에러의 경우에는 기존 페이지를 그대로 노출한다. 대체 UI는 renderFallback이란 Props로 받아와서 렌더링한다.
render() {
const { error, errorCase } = this.state
const { children, renderFallback } = this.props
const renderFallbackErrorCases = ['axiosGetError', 'unknown']
if (errorCase && renderFallbackErrorCases.includes(errorCase)) {
return renderFallback({
error,
errorCase,
onReset: this.resetErrorBoundary,
})
}
return children
}최종 완성 된 GlobalErrorBoundary는 다음과 같다
type GlobalErrorCase =
| "unauthorized"
| "axiosGetError"
| "axiosMutationError"
| "unknown";
export type RenderFallbackProps<ErrorType extends Error = Error> = {
error: ErrorType;
errorCase: GlobalErrorCase;
onReset: (...args: unknown[]) => void;
};
export type RenderFallbackType = <ErrorType extends Error>(
props: RenderFallbackProps<ErrorType>,
) => ReactNode;
type ErrorBoundaryProps = PropsWithRef<
PropsWithChildren<{
onReset?(): void;
renderFallback: RenderFallbackType;
}>
>;
type GlobalErrorBoundaryState =
| { error: null; errorCase: null }
| { error: Error; errorCase: "unknown" }
| {
error: AxiosError<{ message: string }>;
errorCase: "unauthorized" | "axiosGetError" | "axiosMutationError";
};
const initialState: GlobalErrorBoundaryState = {
error: null,
errorCase: null,
};
export class GlobalErrorBoundary extends Component<
PropsWithChildren<ErrorBoundaryProps>,
GlobalErrorBoundaryState
> {
constructor(props: ErrorBoundaryProps) {
super(props);
this.state = {
error: null,
errorCase: null,
};
}
public static getDerivedStateFromError(
error: Error,
): GlobalErrorBoundaryState {
// 다음 렌더링에서 폴백 UI가 보이도록 상태를 업데이트 한다.
if (!error) {
return { error: null, errorCase: null };
}
if (!(error instanceof AxiosError)) {
return { error, errorCase: "unknown" };
}
if (error.response?.status === 401) {
return { error, errorCase: "unauthorized" };
}
if (error.response?.config.method === "get") {
return { error, errorCase: "axiosGetError" };
}
return { error, errorCase: "axiosMutationError" };
}
// error fallback에 전달할 reset handler
resetErrorBoundary = () => {
const { onReset } = this.props;
onReset && onReset();
// ErrorBoundary state를 초기화
this.setState(initialState);
};
public componentDidCatch(error: Error, errorInfo: ErrorInfo) {
// 에러 리포팅 서비스에 에러를 기록할 수 있음
// logErrorToMyService(error, errorInfo)
const { error: errorState, errorCase } = this.state;
if (errorState instanceof AxiosError) {
return errorMesssageHandler(errorState);
}
if (errorCase === "unknown") {
return Toast.show("알 수 없는 에러가 발생했습니다.", { type: "error" });
}
}
render() {
const { error, errorCase } = this.state;
const { children, renderFallback } = this.props;
const renderFallbackErrorCases = ["axiosGetError", "unknown"];
if (errorCase && renderFallbackErrorCases.includes(errorCase)) {
return renderFallback({
error,
errorCase,
onReset: this.resetErrorBoundary,
});
}
return children;
}
}
export default GlobalErrorBoundary;LocalErrorBoundary 생성하기
추가적으로 LocalErrorBoundary를 생성해준다. 다음과 같은 상황을 고려한 것인데 네이버 화면을 예로 들어 설명하려고 한다.
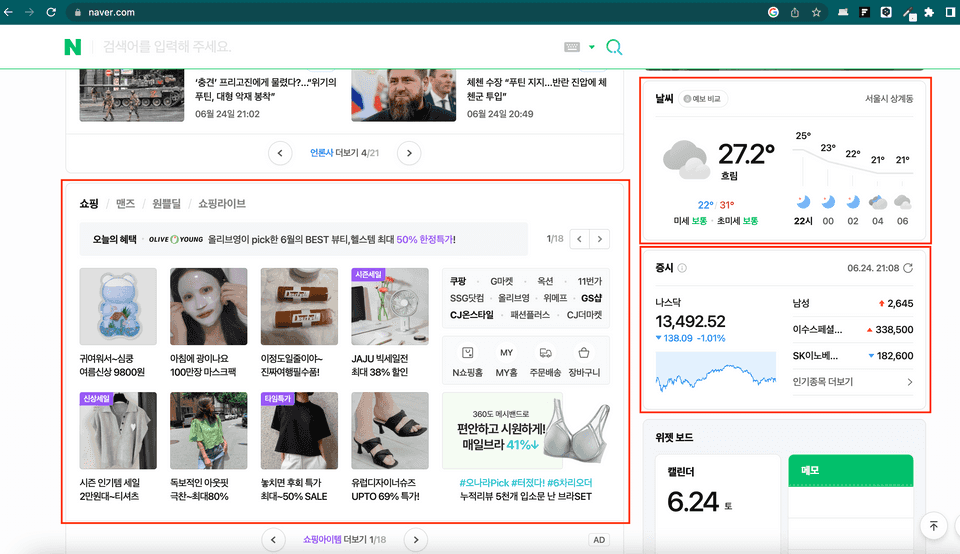
한 화면 안에 날씨, 증시, 쇼핑 등 다양한 정보를 노출하고 있다. 만약 쇼핑과 날씨에 대한 정보는 제대로 받아왔지만 증시 데이터를 받아오는데 에러가 발생 했을 때 GlobalErrorBoundary 만을 사용한다면 화면 전체에 대체 UI가 노출 될 것이다. 그러나 이러한 대처는 안좋은 유저경험을 제공하게 된다. 데이터를 잘 받아온 날씨와 쇼핑 부분은 화면은 정상적으로 노출하고 증시 부분에 대해서만 대체 UI를 제공함으로써 더 나은 UX를 제공할 수 있다.
따라서 이러한 에러의 경계선을 만들어 줄 수 있도록 LocalErrorBoundary를 만들어 적용하고 싶은 부분에 따로 감싸 줄 수 있도록 한다.
type LocalErrorBoundaryState =
| { error: null; errorCase: null }
| { error: Error; errorCase: "shouldRethrow" }
| { error: Error; errorCase: "unknown" }
| {
error: AxiosError<{ message: string }>;
errorCase: "axiosGetError";
};LocalErrorBoundary에서는 unknown 에러와 axiosGetError 만을 캐치하고 나머지 에러는 throw하여 GlobalErrorBoundary에서 처리될 수 있도록 한다.
완성된 LocalErrorBoundary의 코드
type LocalErrorBoundaryProps<ErrorType extends Error = Error> = PropsWithRef<
PropsWithChildren<{
/**
* @description 발생할 수 있는 error에 대한 기준값으로 이 값이 변경되면 error를 초기화한다.
*/
resetKeys?: unknown[];
onReset?(): void;
renderFallback: RenderFallbackType;
onError?(error: ErrorType, info: ErrorInfo): void;
}>
>;
type LocalErrorBoundaryState =
| { error: null; errorCase: null }
| { error: Error; errorCase: "shouldRethrow" }
| { error: Error; errorCase: "unknown" }
| {
error: AxiosError<{ message: string }>;
errorCase: "axiosGetError";
};
const initialState: LocalErrorBoundaryState = {
error: null,
errorCase: null,
};
export class BaseErrorBoundary extends Component<
PropsWithChildren<LocalErrorBoundaryProps>,
LocalErrorBoundaryState
> {
state = initialState;
updatedWithError = false;
constructor(props: LocalErrorBoundaryProps) {
super(props);
this.state = {
error: null,
errorCase: null,
};
}
public static getDerivedStateFromError(
error: Error,
): LocalErrorBoundaryState {
// 다음 렌더링에서 폴백 UI가 보이도록 상태를 업데이트 한다.
if (!error) {
return { error: null, errorCase: null };
}
if (!(error instanceof AxiosError)) {
return { error, errorCase: "unknown" };
}
if (error.response?.config.method === "get") {
return { error, errorCase: "axiosGetError" };
}
return { error, errorCase: "shouldRethrow" };
}
resetState() {
this.updatedWithError = false;
this.setState(initialState);
}
// error fallback에 전달할 reset handler
resetErrorBoundary = () => {
const { onReset } = this.props;
onReset && onReset();
// ErrorBoundary state를 초기화
this.resetState();
};
public componentDidCatch(error: Error, errorInfo: ErrorInfo) {
// 에러 리포팅 서비스에 에러를 기록할 수 있음
// logErrorToMyService(error, errorInfo)
const { error: errorState, errorCase } = this.state;
const { onError } = this.props;
if (errorCase === "axiosGetError") {
onError && onError(error, errorInfo);
return errorMesssageHandler(errorState);
}
if (errorCase === "unknown") {
onError && onError(error, errorInfo);
return Toast.show("알 수 없는 에러가 발생했습니다.", { type: "error" });
}
if (errorCase === "shouldRethrow") {
throw error;
}
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps: LocalErrorBoundaryProps) {
const { error } = this.state;
const { resetKeys } = this.props;
if (error === null) {
return;
}
if (!this.updatedWithError) {
this.updatedWithError = true;
return;
}
if (isDifferentArray(prevProps.resetKeys, resetKeys)) {
this.resetErrorBoundary();
}
}
render() {
const { error, errorCase } = this.state;
const { children, renderFallback } = this.props;
if (error && errorCase !== "shouldRethrow") {
return renderFallback({
error,
errorCase,
onReset: this.resetErrorBoundary,
});
}
return children;
}
}
export const LocalErrorBoundary = forwardRef<
{ reset(): void },
ComponentPropsWithoutRef<typeof BaseErrorBoundary>
>((props, resetRef) => {
const ref = useRef<BaseErrorBoundary>(null);
useImperativeHandle(resetRef, () => ({
reset: () => ref.current?.resetErrorBoundary(),
}));
return <BaseErrorBoundary {...props} ref={ref} />;
});
LocalErrorBoundary.displayName = "LocalErrorBoundary";추가적으로 LocalErrorBoundary에서는 옵셔널하게 onError와 resetKeys라는 Props를 받을 수 있도록 하여 onError를 통해 에러 발생시에 취하고 싶은 추가적인 엑션을 설정하거나, resetKeys가 변경되면 에러가 리셋될 수 있도록 했다.
실제 서비스에 적용된다면 어떤 모습일까?
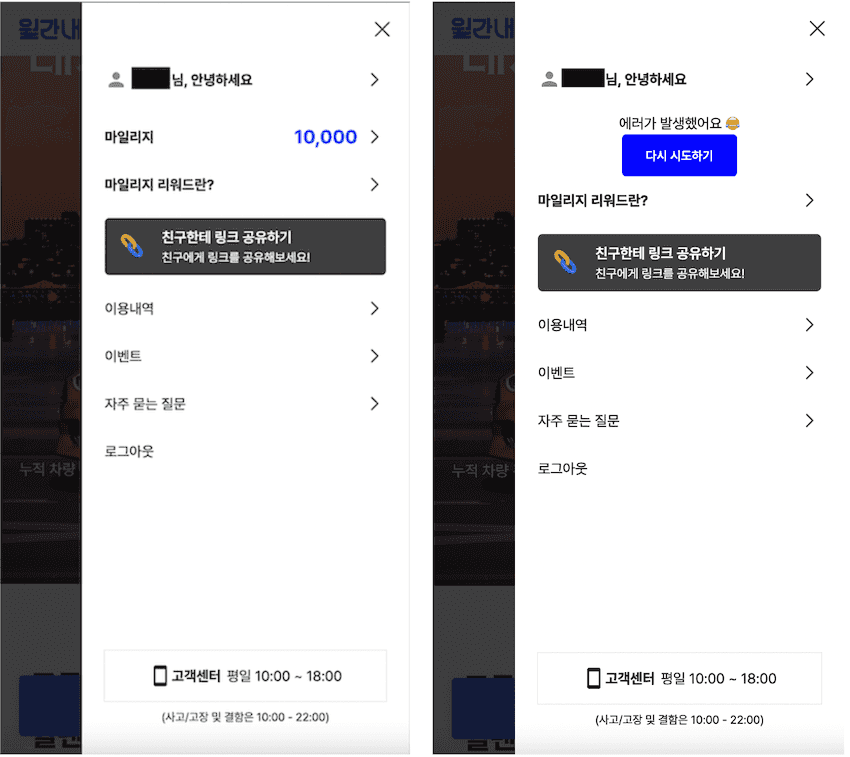
서비스의 메뉴 목록 중에는 아래의 이미지에서 보여지듯 유저의 마일리지를 실시간으로 노출해주는 항목이 있다. 만약 어떠한 이유로 인해 마일리지를 값을 받아오는 API 통신에서 에러가 발생 했을 때 메뉴 전체가 대체UI로 노출된다면 유저는 어디로도 이동할 수 없는 진퇴양난의 상황에 빠지게 될 수도 있다😫. 하지만 이러한 경우에 에러가 발생할 수 있는 컴포넌트만 LocalErrorBoundary로 감싸준다면? 짜잔- 오른쪽의 화면처럼 에러가 발생한 마일리지 메뉴 항목만 대체 UI를 노출할 수 있다.
이제 서버와 통신하는 비동기 코드를 일일히 try-catch로 감싸는 수고로움 없이 우아하게 에러를 다룰 수 있게 되었다.
사실 조금만 찾아보면 여러가지 편의 기능을 제공하는 ErrorBoundary 라이브러리들이 존재한다. react-error-boundary도 있고, 토스에서 제공하는 라이브러리인 toss/slash에도 @toss/error-boundary가 있다. 내가 작성한 ErrorBoundary도 해당 라이브러리들의 코드를 많이 참고했다. 라이브러리를 설치해 사용하면 보다 손쉽게 사용이 가능하지만 라이브러리의 코드를 뜯어보고 직접 만들어 사용해보면 내부동작을 이해하고 사용할 수 있어 공부가 되기도 하고 각자의 서비스에 맞게 커스텀이 가능하니, 이 글을 읽는 누군가도 가능한 라이브러리의 코드는 참고용으로 보고 직접 만들어보길 권장해본다😋